Heard Health & Production Medicine
IgG content and bacteriological quality of colostrum from Dutch HF and Belgian Blue cows
G. Hoflack1, P.A.A. Penterman1, G. Vertenten2, W.A. Schaap3, F.H.J. Van Hagen4, B. Sustronck1
Belgian Blue cows have significantly higher colostrum quality and lower bacterial load in their colostrum in comparison to Dutch Holstein Friesian cows.

Decrease in type G immunoglobulins in the colostrum of dairy cows and suckling cows during the first 5 days after calving
Clara Bourel1, Raphaëlle Deffrenne1, Geert Vertenten2
This study showed a faster decrease in IgG concentration for dairy breeds than beef breeds. The total mass of IgG produced in transition milk remains considerable. This should encourage dairy farmers to distribute at least transition milk to the calf during the first days of life or to extend the distribution of 250 mL colostrum or transition milk (2nd or 3rd milking) over the first days of life.

On-farm evaluation of the neonatal hygiene management protocol using ATP bioluminescence
P.A.A. Penterman1, S. Plekkenpol3, M. Andringa4, H. Kuijk1, G. Vertenten2 and B. Sustronck1
Clean calf pen does not correlate with clean colostrum/feeding equipment. ATP bioluminescence measurements can be used as an on-farm screening tool to evaluate the cleaning and disinfection protocol used in the calf raising units on Dutch dairy farms.

Herd Health Planning for veterinarians using on-farm automated monitoring systems: an effectual marketing pilot study
Liz Cresswell1, Monica Miravalle1, Monika Ptaszynska-Sutton1
Three main feedback themes were identified to inform the future development of a new service, which brings vets and farmers together using the data insights produced by an on-farm automated monitoring system.

Colostrum collection using robotic milking systems: impact on immunoglobulin concentration
P.A.A. Penterman1, G. Hoflack1, G. Vertenten2, W.A. Schaap3 , Eva Haas4 and B. Sustronck1
Robotic milking systems can significantly reduce the IgG concentration in bovine colostrum.
Dilution of the colostrum due to incomplete removal of the flushing fluid in the separation lines of the robotic milking system could be at the base of this observation.
After robotic colostrum harvest, measurement of the IgG concentration (e.g. using Brix refractometry) is recommended to avoid the administration of poor quality colostrum to new-born calves. Ideally, colostrum is hand milked to avoid this probable dilution.

Colostrum collection using robotic milking systems: impact on microbiological quality
P.A.A. Penterman1, G. Hoflack1, N. Botteldoorn2, G. Vertenten3, W.A. Schaap4, L. Gille1 and B. Sustronck1
The microbiological quality of colostrum is significantly reduced when robotic milking systems are used for colostrum collection.
Insufficient cleaning after passage of the viscous colostrum or mastitis milk in the separation lines of the robotic milking system could be at the base of this observation.
The degree of this negative effect of robotic milking on the microbiological quality of the colostrum is farm dependent.
When using robotic milking to collect colostrum, special attention needs to be paid to hygienic measures (e.g. cleaning and disinfection) to prevent excessive bacterial contamination during colostrum collection. Ideally, colostrum is hand milked to avoid this contamination.

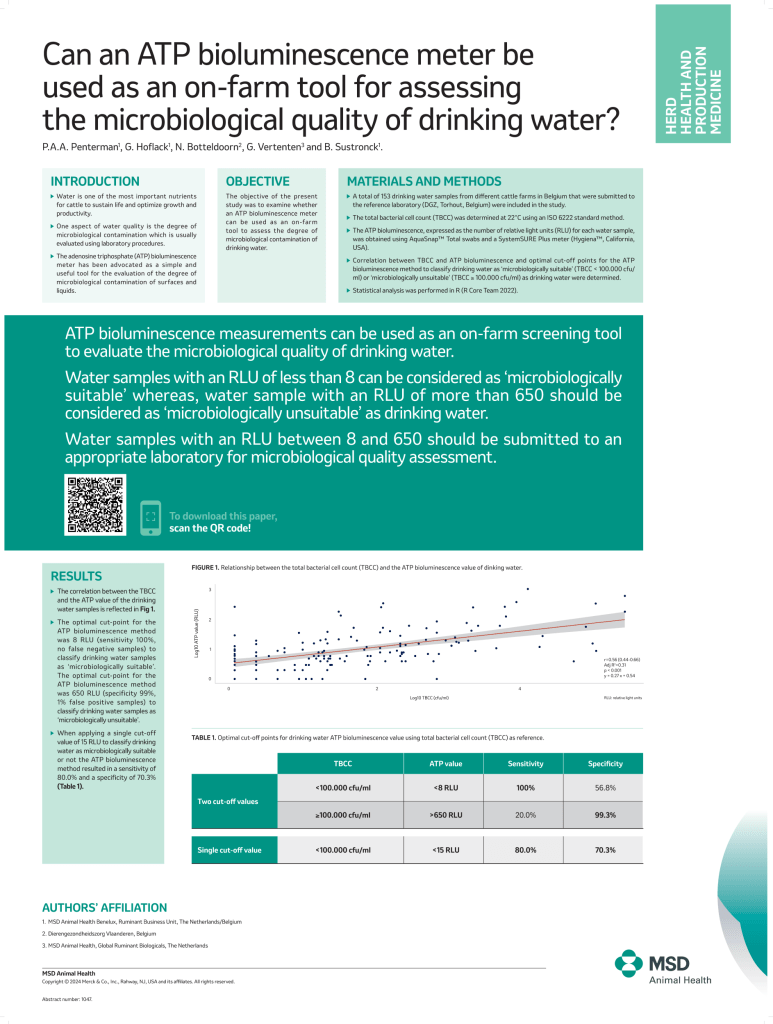
Can an ATP bioluminescence meter be used as an on-farm tool for assessing the microbiological quality of drinking water?
P.A.A. Penterman1, G. Hoflack1, N. Botteldoorn2, G. Vertenten3 and B. Sustronck1.
ATP bioluminescence measurements can be used as an on-farm screening tool to evaluate the microbiological quality of drinking water.
Water samples with an RLU of less than 8 can be considered as ‘microbiologically suitable’ whereas, water sample with an RLU of more than 650 should be considered as ‘microbiologically unsuitable’ as drinking water.
Water samples with an RLU between 8 and 650 should be submitted to an appropriate laboratory for microbiological quality assessment.
Effect of storage conditions and initial bacterial load on the microbiological quality of colostrum
P.A.A. Penterman1, G. Hoflack1, N. Botteldoorn2, G. Vertenten3, W.A. Schaap4, E. Haas5, B. Sustronck1
Storing colostrum at temperatures above 4°C should be avoided.
Storage of colostrum with a high initial bacterial load (TBCC ≥1,000,000 cfu/ml and TCC ≥1,000 cfu/ml) at 4°C for more than 48 hours results in a significant increase in TBCC and TCC.
Besides the storage of colostrum at an appropriate temperature, hygienic harvesting of colostrum is of utmost importance for its microbiological quality.

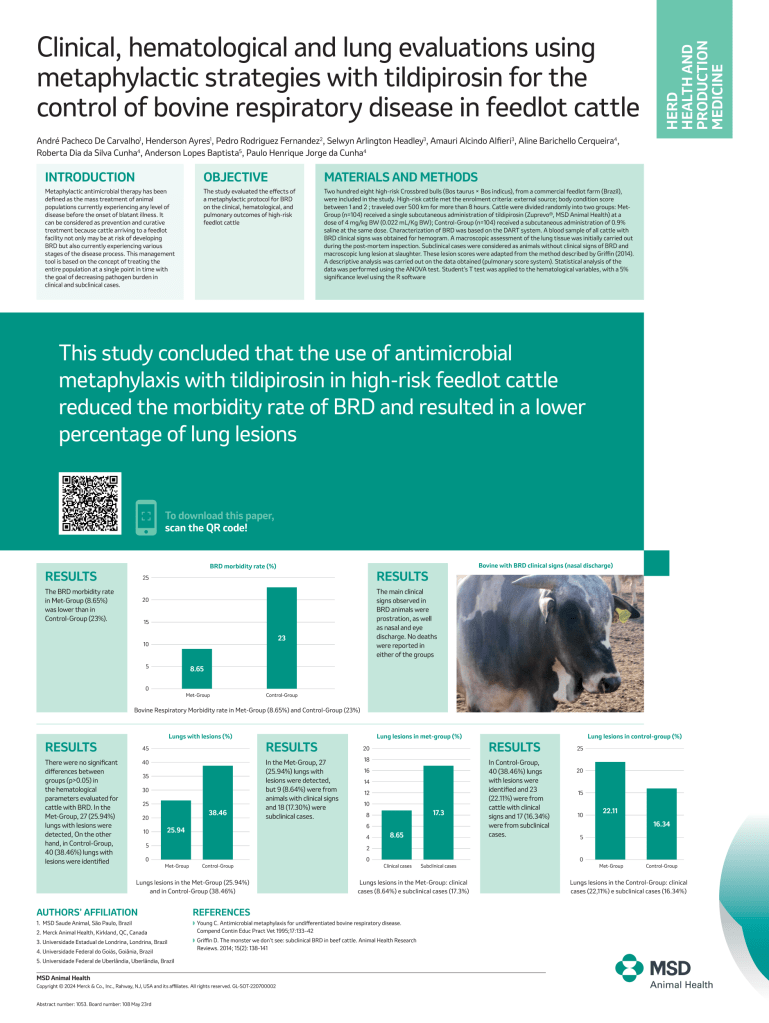
Clinical, hematological and lung evaluations using metaphylactic strategies with tildipirosin for the control of bovine respiratory disease in feedlot cattle
André Pacheco De Carvalho1, Henderson Ayres1, Pedro Rodriguez Fernandez2, Selwyn Arlington Headley3, Amauri Alcindo Alfieri3, Aline Barichello Cerqueira4, Roberta Dia da Silva Cunha4, Anderson Lopes Baptista5, Paulo Henrique Jorge da Cunha4
This study concluded that the use of antimicrobial metaphylaxis with tildipirosin in high-risk feedlot cattle reduced the morbidity rate of BRD and resulted in a lower percentage of lung lesions
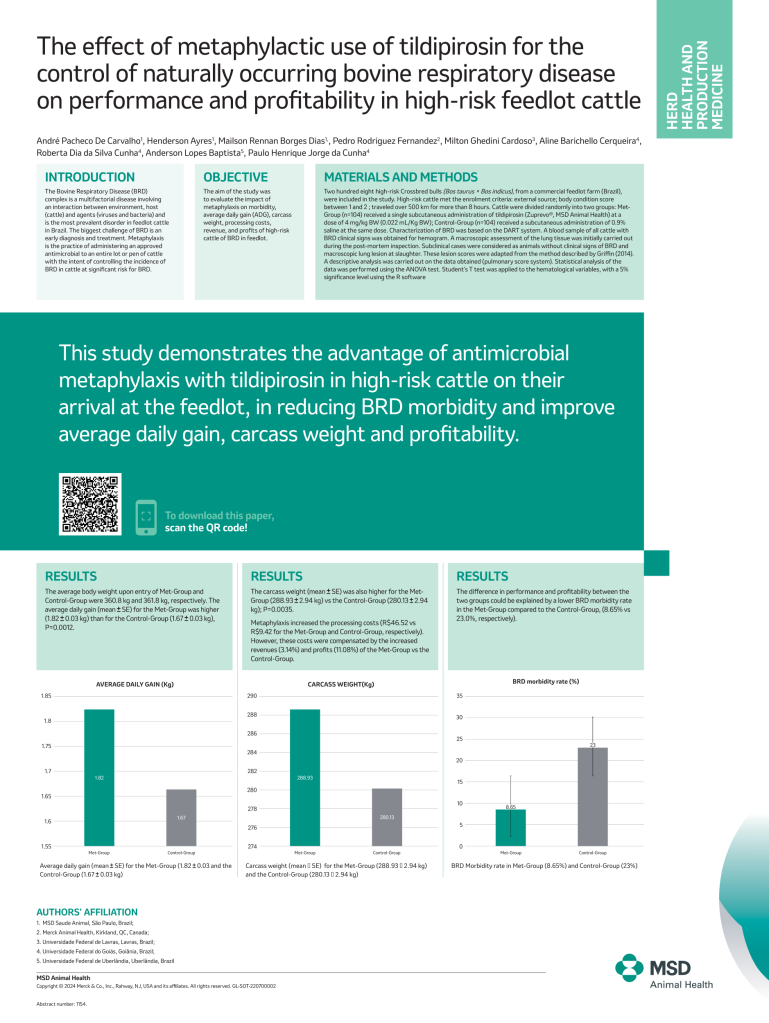
The effects of metaphylactic use of tildiprirosin for the control of naturally occurring bovine respiratory disease on performance and profitability in high-risk feedlot cattle
André Pacheco De Carvalho1, Henderson Ayres1, Mailson Rennan Borges Dias1, Pedro Rodriguez Fernandez2, Milton Ghedini Cardoso3, Aline Barichello Cerqueira4, Roberta Dia da Silva Cunha4, Anderson Lopes Baptista5, Paulo Henrique Jorge da Cunha4
This study demonstrates the advantage of antimicrobial metaphylaxis with tildipirosin in high-risk cattle on their arrival at the feedlot, in reducing BRD morbidity and improve average daily gain, carcass weight and profitability.
Effect of ancillary anti-inflammatory treatment of mild clinical mastitis cases in dairy cows
Hernan Bertotti1, Martin Pol2, Guillermo Gargantini3, Jantijn Swinkels4, Pedro Rodriguez Fernandez5, Luciano Borda3
Dairy cows with mild clinical mastitis (CM1) treated with transdermal flunixin meglumine in conjunction with IMM antimicrobial therapy had lower SCC at day 21 and reduced the number of days with low rumination than cows treated with the IMM alone.

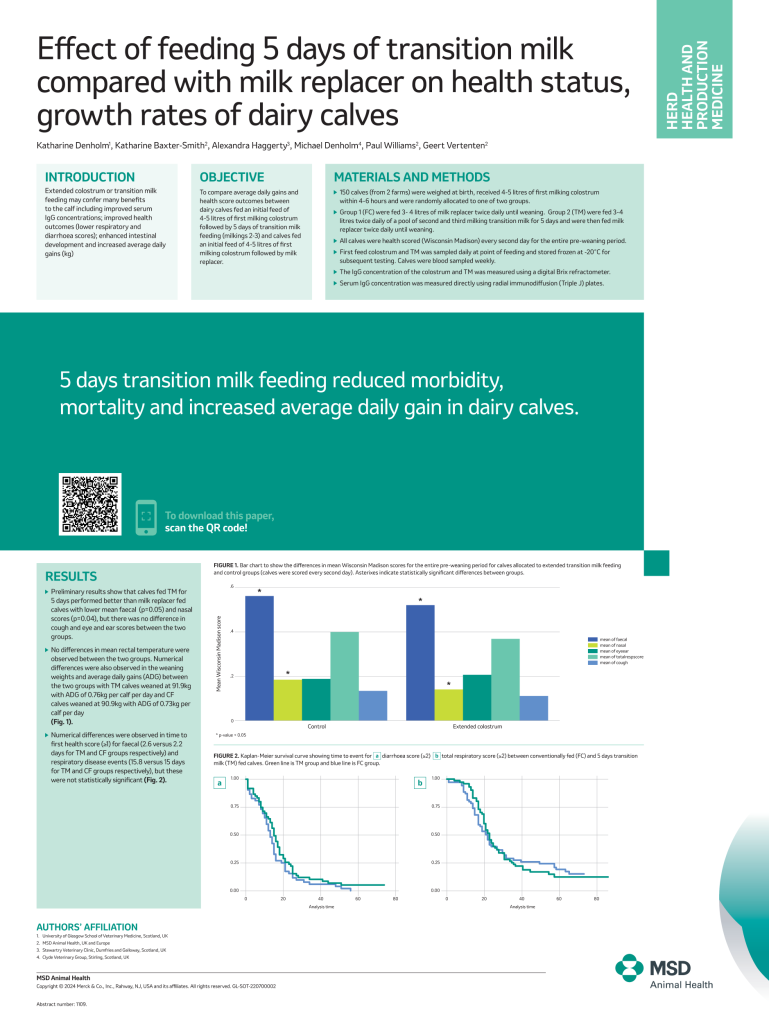
Effect of feeding 5 days of transition milk compared with milk replacer on health status, growth rates of dairy calves
Katharine Denholm1, Katharine Baxter-Smith2, Alexandra Haggerty3, Michael Denholm4, Paul Williams2, Geert Vertenten2
5 days transition milk feeding reduced morbidity,
mortality and increased average daily gain in dairy calves.
Prevalence, biosecurity and risk management of bovine coronavirus infections on white and rose veal and diary source beef calf farms in Europe
Anna Catharina Berge1, Geert Vertenten2
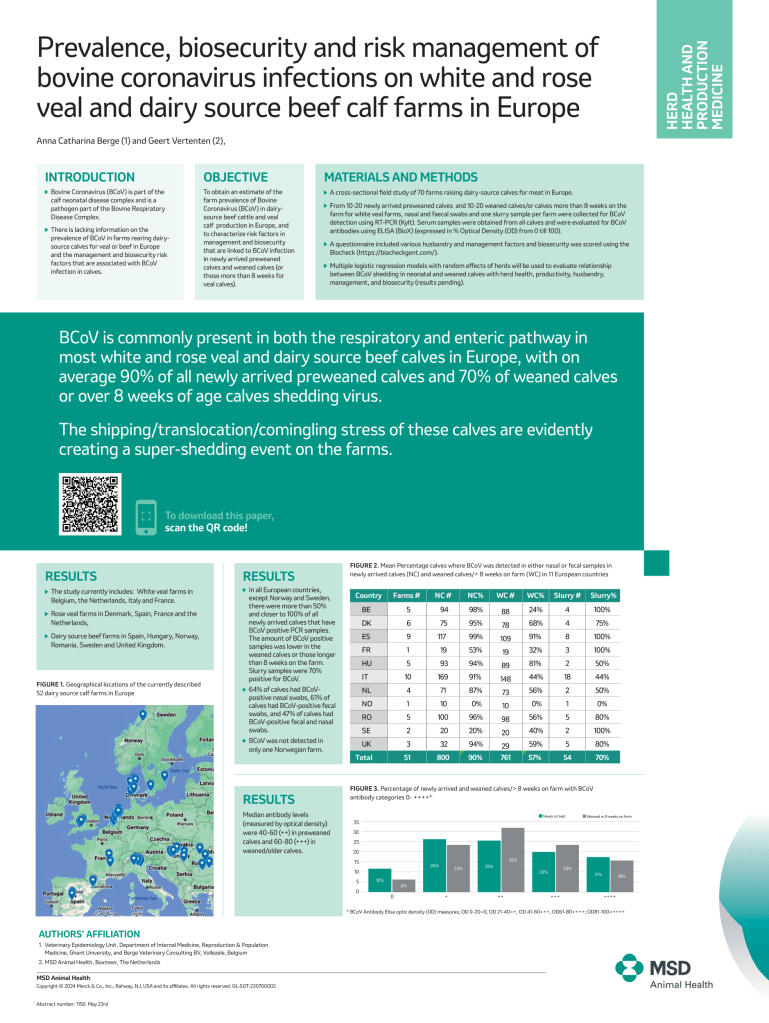
BCoV is commonly present in both the respiratory and enteric pathway in most white and rose veal and dairy source beef calves in Europe, with on average 90% of all newly arrived preweaned calves and 70% of weaned calves or over 8 weeks of age calves shedding virus.
The shipping/translocation/comingling stress of these calves are evidently creating a super-shedding event on the farms.
The effect of colostrum supplementation from Rotavec vaccinated dams during the first 5 days of life on calf health, enteric pathogen shedding and immunological response
Anna Catharina Berge1, Pleun Penterman2, Iris Kolkman3, Geert Vertenten2
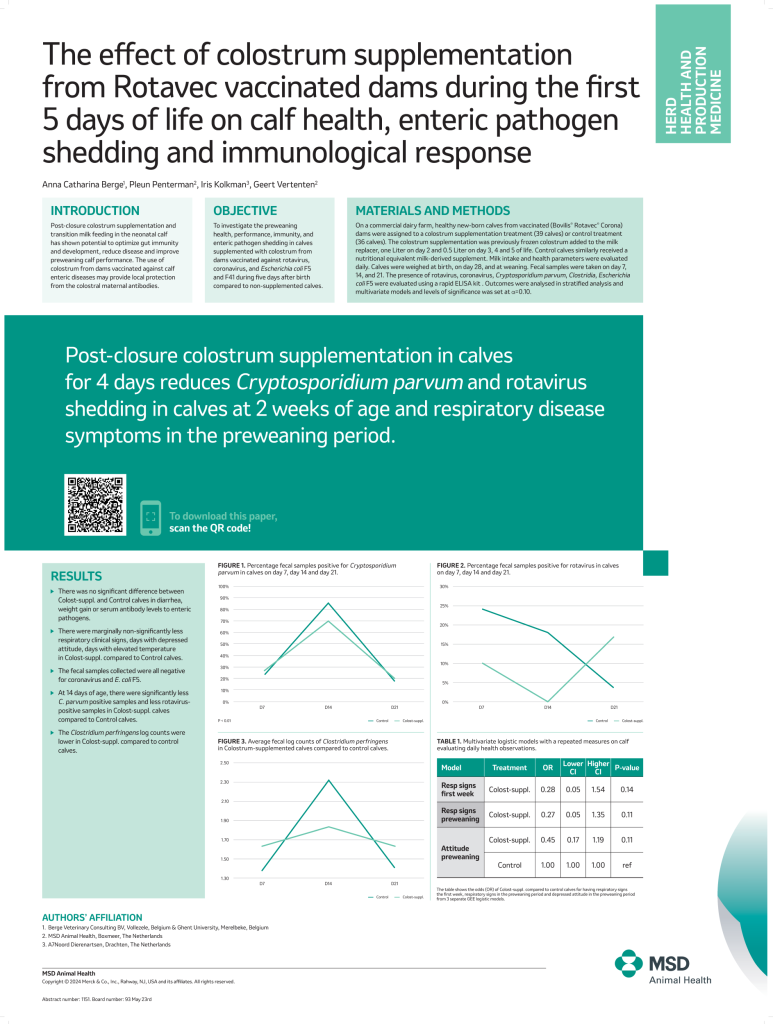
Post-closure colostrum supplementation in calves
for 4 days reduces Cryptosporidium parvum and rotavirus shedding in calves at 2 weeks of age and respiratory disease
symptoms in the preweaning period.
Effect of time of antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory therapy on the recovery process of feedlot cattle from an induced bovine respiratory disease model
Diego Moya1, Kiah Simpson1, Nathan Erickson1, Emily Snyder1, John Ellis2, John Campbell1, Samuel Wauer3, Jason Nickell4, Pedro Rodriguez3
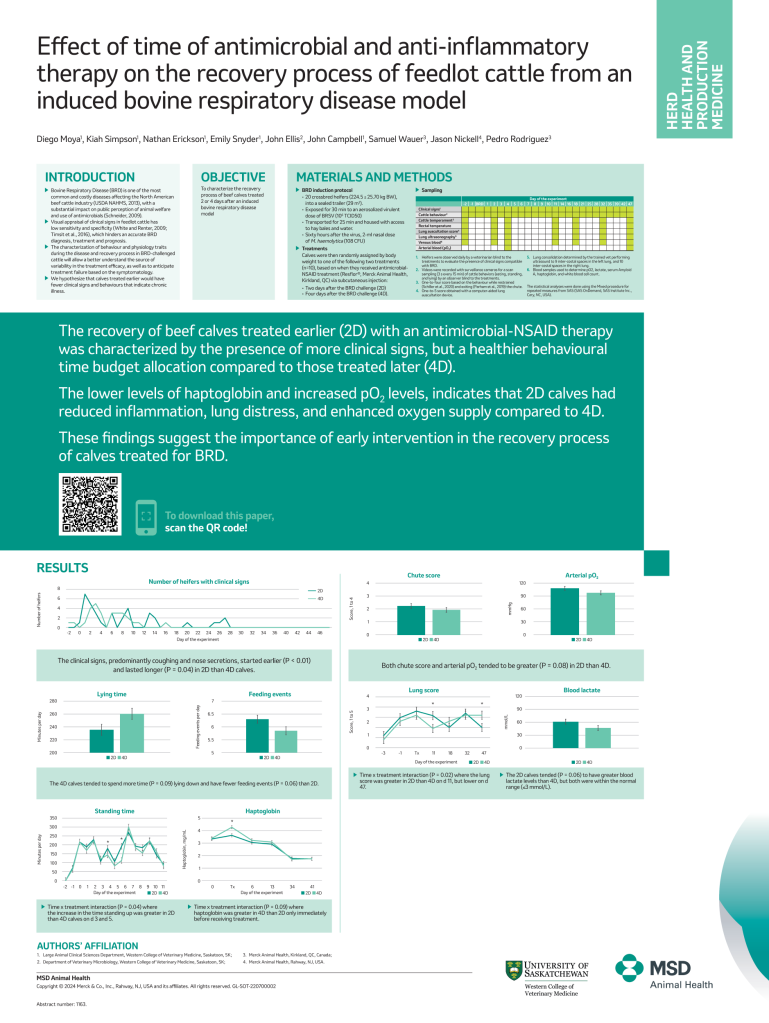
The recovery of beef calves treated earlier (2D) with an antimicrobial-NSAID therapy was characterized by the presence of more clinical signs, but a healthier behavioural time budget allocation compared to those treated later (4D).
The lower levels of haptoglobin and increased pO2 levels, indicates that 2D calves had reduced inflammation, lung distress, and enhanced oxygen supply compared to 4D.
These findings suggest the importance of early intervention in the recovery process of calves treated for BRD.
Farmer’s Perception About Bovine Respiratory Disease (BRD) On Their Farms And Its Real Impact
João Paulo Silva1, Alfredo Teixeira2, Paulo Capêlo1, André Martins1, Miguel Quaresma3, Ana Cláudia Coelho3
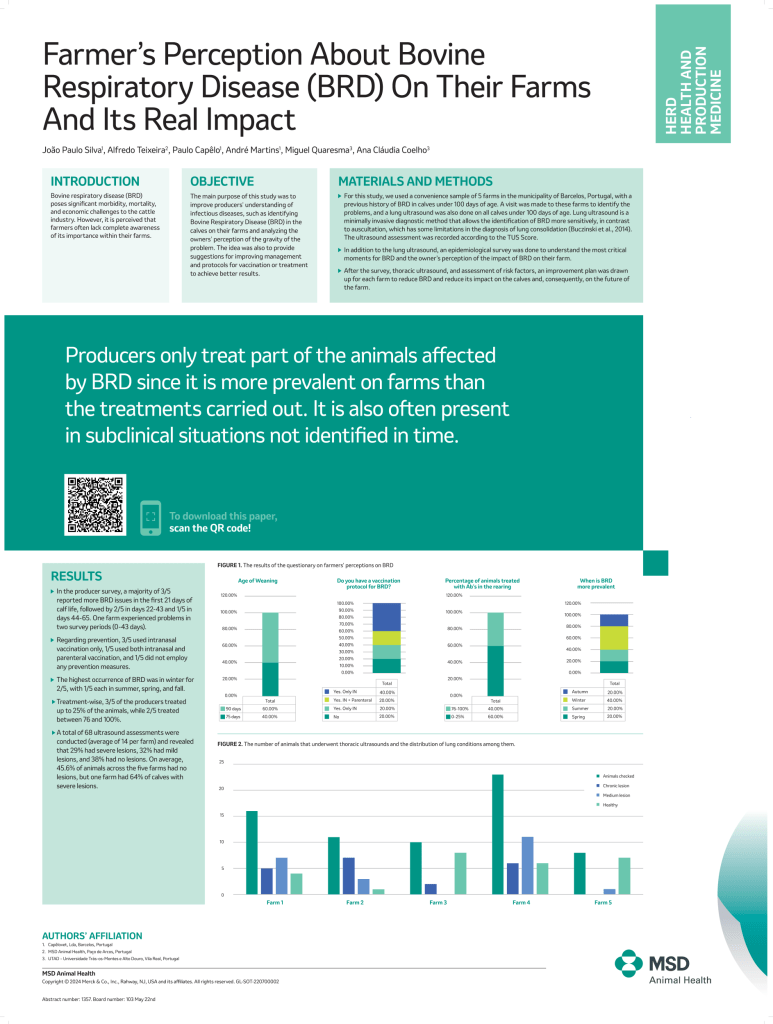
Producers only treat part of the animals affected
by BRD since it is more prevalent on farms than
the treatments carried out. It is also often present
in subclinical situations not identified in time.
Comparative Evaluation of Three Tests for Failure of Passive Transfer and Association with BRD and NCD Pathogen-Specific Antibodies in Neonatal Calves
Egon Thesing1; Bart Sustronck2; Geert Vertenten3
IgG ELISA-Munich and IgG ELISA-BioX methods have comparable performance in detecting FPT, while the Brix method showed lower accuracy.
There is a strong association between passive immunity transfer
and pathogen-specific antibodies which highlights the importance of adequate passive transfer for calf health and immunity.

Comparative use of Automated Behavior Monitoring System versus on-Farm Standard Operation Procedure for youngstock health in a commercial dairy farm
Tejero, Carolina1, 2; Sales, MªLuz2; Elvira, Laura1; Friedman, Eran3; Preto, André3
In conclusion, from a practical perspective, SenseHubTM Dairy Youngstock delivered insights that helped the farmer & veterinarian to have an earlier BRD diagnosis and lower prevalence of lung lesions at weaning. This had a positive impact on survival rates on the farm.


